How to use HDF5 to handle large quantities¶
The NOMAD schemas and processed data system are designed to describe and manage intricate hierarchies of connected data. This is ideal for metadata and lots of small data quantities, but does not work for large quantities. Quantities are atomic and are always managed as a whole; there is currently no functionality to stream or splice large quantities. Consequently, tools that produce or work with such data cannot scale.
To address the issue, the option to use auxiliary storage systems optimized for large
data is implemented. In the following we discuss two quantity types to enable the writing
of large datasets to HDF5: HDF5Reference and HDF5Dataset. These are defined in
nomad.datamodel.hdf5. Another class called HDF5Normalizer defined in
nomad.datamodel.metainfo.basesections can be inherited
and used directly in a yaml schema.
HDF5Reference¶
HDF5Reference is a metainfo quantity type intended to reference datasets in external raw HDF5 files. It is assumed that the dataset exists in an HDF5 file and the reference is assigned to this quantity. Static methods to read from and write to an HDF5 file are implemented. The following example illustrates how to use these.
from nomad.datamodel import ArchiveSection
from nomad.datamodel.hdf5 import HDF5Reference
class LargeData(ArchiveSection):
value = Quantity(type=HDF5Reference)
The writing and reading of quantity values to and from an HDF5 file occur during
processing. For illustration purposes, we mock this by creating ServerContext. Furthermore,
we use this section definition for the data sub-section of EntryArchive.
import numpy as np
from nomad.datamodel import EntryArchive, EntryMetadata
from nomad.datamodel.context import ServerContext
from nomad.files import StagingUploadFiles
from nomad.processing import Upload
upload_files = StagingUploadFiles(upload_id='test_upload', create=True)
upload = Upload(upload_id='test_upload')
upload_files.add_rawfiles('external.h5')
context = ServerContext(upload=upload)
archive = EntryArchive(
m_context=context,
metadata=EntryMetadata(upload_id=upload.upload_id, entry_id='test_entry'),
data=LargeData(),
)
data = np.eye(3)
path = 'external.h5#path/to/data'
HDF5Reference.write_dataset(archive, data, path)
archive.data.value = path
HDF5Reference.read_dataset(archive, path)
array([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])
We use write_dataset to write our data into a raw HDF5 file in test_upload with the
filename and dataset location in path. Additionally, archive is required to resolve the
upload metadata. We then assign the reference to the dataset to value. To reference a
file in another upload, follow the same form for
reference values e.g.
/uploads/<upload_id>/raw/large_data.hdf5#group/large_field.
Important
When reassigning a different value for an HDF5 archive quantity, it is necessary that the data attributes (shape and type) are preserved.
To read a dataset, use read_dataset and provide a reference. This will return the value
cast in the type of the dataset.
HDF5Dataset¶
To use HDF5 storage for archive quantities, one should use HDF5Dataset.
from nomad.datamodel.hdf5 import HDF5Dataset
class LargeData(ArchiveSection):
value = Quantity(type=HDF5Dataset)
The assigned value will also be written to the archive HDF5 file and serialized as
/uploads/test_upload/archive/test_entry#/data/value.
To read the dataset, one shall use the context manager with to ensure the file is closed properly when done.
archive.data.value = np.ones(3)
serialized = archive.m_to_dict()
serialized['data']['value']
# '/uploads/test_upload/archive/test_entry#/data/value'
deserialized = archive.m_from_dict(serialized, m_context=archive.m_context)
with deserialized.data.value as dataset:
print(dataset[:])
# array([1., 1., 1.])
It is possible to assign to an archive quantity an array or another archive quantity. In the second case, the dataset created in the HDF5 file will contain a link and not a copy of the array:
from nomad.datamodel.hdf5 import HDF5Dataset
class LargeData(ArchiveSection):
value_1 = Quantity(type=HDF5Dataset)
value_2 = Quantity(type=HDF5Dataset)
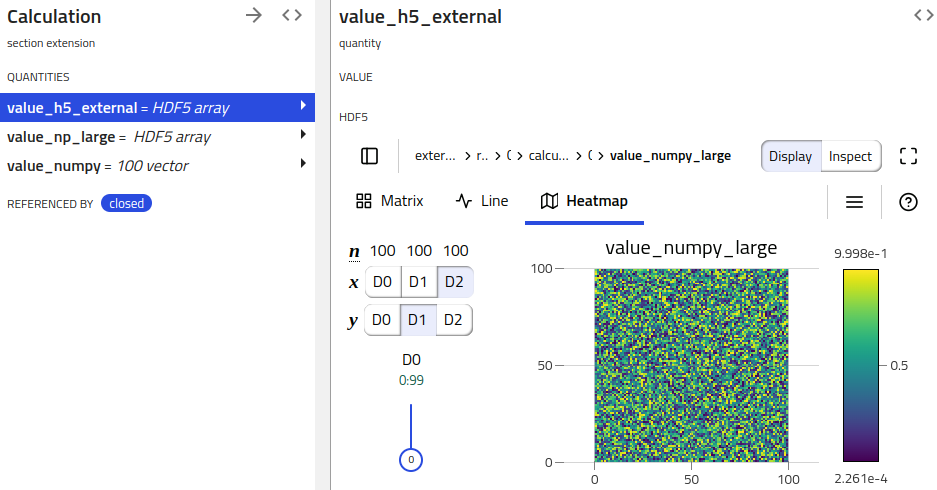
Visualizing archive HDF5 quantities¶
NOMAD clients (e.g. NOMAD UI) can pick up on these HDF5 serialized quantities and provide respective functionality (e.g. showing a H5Web view).
When multiple quantities need to be displayed in the same plot, some attributes in the HDF5 file groups are needed, in order for h5web to be able to render a plot. The H5WebAnnotation class contains the attributes to be included in the groups (dataset) of HDF5 file, provided as section (quantity) annotations.
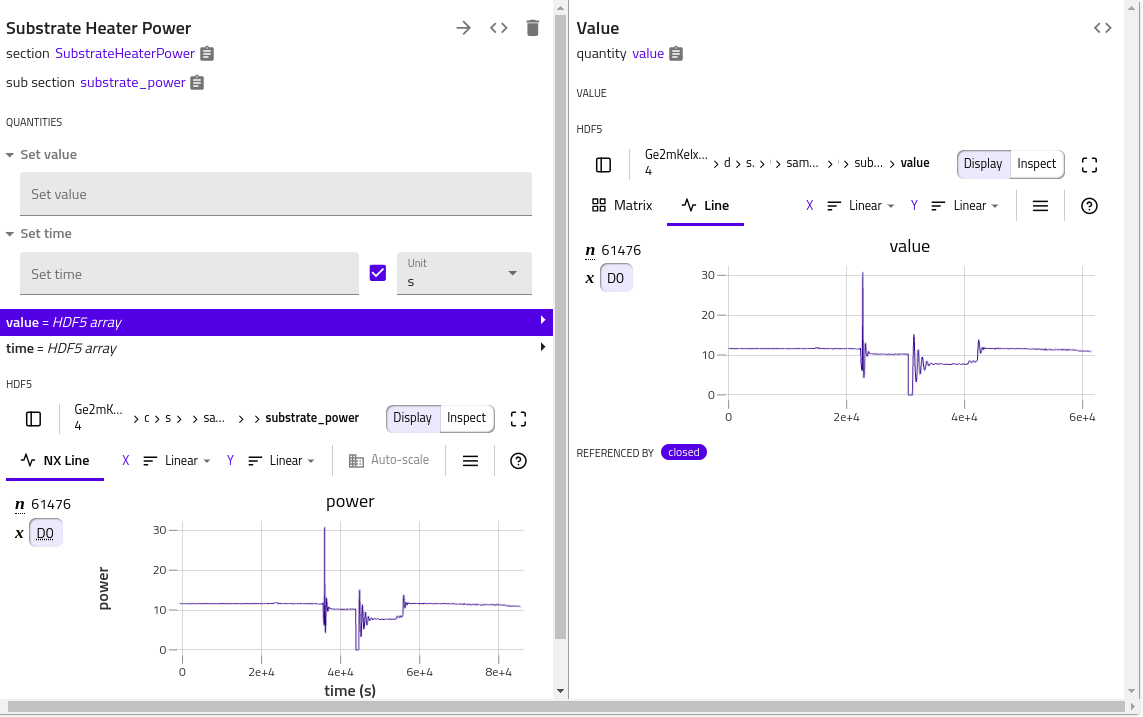
In the following example, the value quantity has a dedicated default h5web rendering.
Adding some annotation in the corresponding section would trigger another plot rendering, where value vs. time plot is shown. The errors to the dataset can be specified by errors
annotation.
class MySection(ArchiveSection):
m_def = Section(a_h5web=H5WebAnnotation(axes='time', signal='value'))
value = Quantity(
type=HDF5Dataset,
unit='dimensionless',
shape=[],
a_h5web=H5WebAnnotation(
long_name='power',
errors='value_e'
),
)
value_e = Quantity(
type=HDF5Dataset
)
time = Quantity(
type=HDF5Dataset,
unit='s'
shape=[]
)
To include plots corresponding to sub sections, one can provide a list of the section
paths to the annotation paths. The following example will trigger a rendering of the plot
corresponding to the first my_sub section. One can also use wildcards * to include
all sub sections and ** to recursively search sub sections.
class MySubSection(ArchiveSection):
m_def = Section(a_h5web=H5WebAnnotation(axes='x', signal='y'))
x = Quantity(
type=HDF5Reference
)
y = Quantity(
type=HDF5Reference
)
class MySection(ArchiveSection):
m_def = Section(a_h5web=H5WebAnnotation(paths=['my_sub/0']))
my_sub = SubSection(sub_section=MySubSection, repeats=True)
Metadata for large quantities¶
Attention
This will be implemented and documented soon.